Google Introduces Enhanced Security Measures for Chrome’s Agentic Features
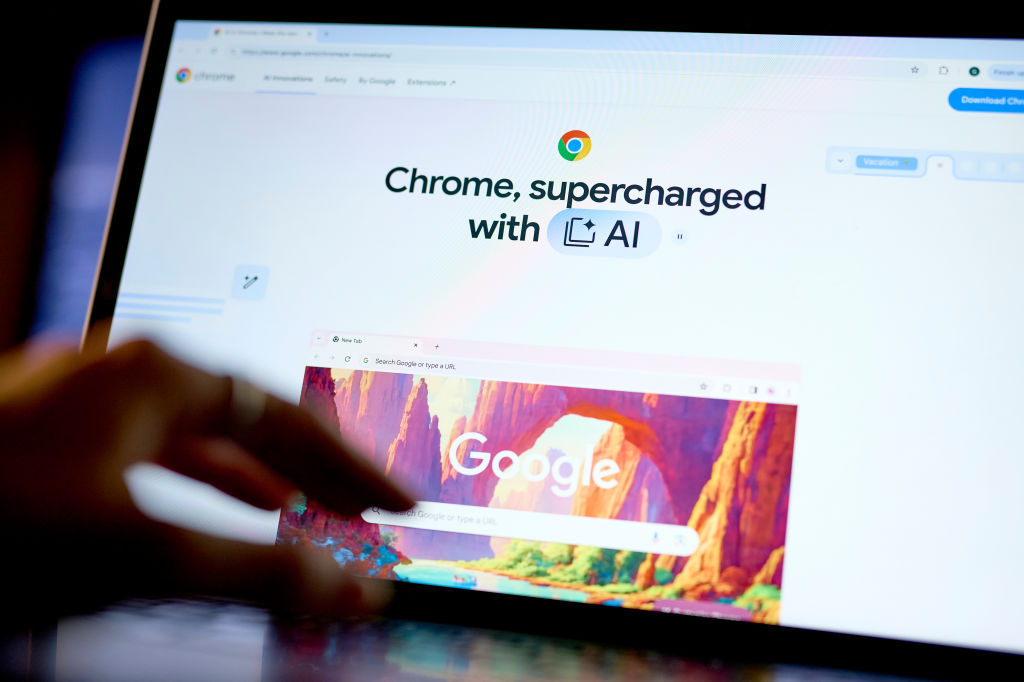
In response to the rising use of agentic capabilities in web browsers, Google has unveiled robust security enhancements for its Chrome browser. These features, designed to perform tasks on behalf of users—such as making reservations or shopping—also pose potential risks including data breaches and financial loss. Google plans to roll out these improvements in the coming months, following a preview in September.
The tech giant’s strategy centers around sophisticated observer models and user consent protocols to bolster security. Central to this approach is the User Alignment Critic, developed using the Gemini system. This model assesses task proposals generated by a planner model, ensuring that recommended actions align with user objectives. Importantly, the critic model only accesses metadata, safeguarding user data from unwanted exposure.
To mitigate risks associated with accessing dubious sites, Google has introduced Agent Origin Sets. This feature restricts agent access to designated read-only and read-write origins, allowing the agent to engage only with permissible content. For instance, while a shopping site’s product listings are accessible, distracting banner ads remain off-limits. This delineation aims to minimize the potential for cross-origin data leaks, enhancing user safety during transactions.
Furthermore, Google is implementing an additional layer of protection through URL navigation checks via another observer model, which aims to prevent the browser from accessing harmful web pages generated by its AI models.
In an effort to prioritize user control, Google is allowing users to authorize sensitive actions directly. Tasks involving sensitive data—such as banking or medical information—will require explicit user consent. In cases where authentication is necessary, users will be prompted to allow Chrome to access their password manager. Notably, the model will not have direct access to sensitive password data, ensuring enhanced privacy.
Additionally, Google has introduced a prompt-injection classifier to thwart unwanted automated actions, and it continues to test its agentic capabilities against simulated attacks devised by cybersecurity researchers.
As web security becomes increasingly vital, other browser developers, like Perplexity, are also exploring new strategies. Earlier this month, Perplexity launched an open-source content detection model aimed at countering prompt injection threats for agentic technologies.